Is organic better than natural

Nutrition and healthy eating
Organic foods: Are they safer? More nutritious?
Discover the difference between organic foods and their traditionally grown counterparts when it comes to nutrition, safety and price.
By Mayo Clinic StaffOnce found only in health food stores, organic food is now a common feature at most grocery stores. And that's made a bit of a problem in the produce aisle.
For example, you can pick an apple grown with usual (conventional) methods. Or you can pick one that's organic. Both apples are firm, shiny and red. They both provide vitamins and fiber. And neither apple has fat, salt or cholesterol. Which should you choose? Get the facts before you shop.
What is organic farming?
The word "organic" means the way farmers grow and process farming (agricultural) products. These products include fruits, vegetables, grains, dairy products such as milk and cheese, and meat. Organic farming practices are designed to meet the following goals:
- Improve soil and water quality
- Cut pollution
- Provide safe, healthy places for farm animals (livestock) to live
- Enable natural farm animals' behavior
- Promote a self-sustaining cycle of resources on a farm
Materials or methods not allowed in organic farming include:
- Artificial (synthetic) fertilizers to add nutrients to the soil
- Sewage sludge as fertilizer
- Most synthetic pesticides for pest control
- Using radiation (irradiation) to preserve food or to get rid of disease or pests
- Using genetic technology to change the genetic makeup (genetic engineering) of crops, which can improve disease or pest resistance, or to improve crop harvests
- Antibiotics or growth hormones for farm animals (livestock)
Organic crop farming materials or practices may include:
- Plant waste left on fields (green manure), farm animals' manure or compost to improve soil quality
- Plant rotation to keep soil quality and to stop cycles of pests or disease
- Cover crops that prevent wearing away of soil (erosion) when sections of land aren't in use and to plow into soil for improving soil quality
- Mulch to control weeds
- Insects or insect traps to control pests
- Certain natural pesticides and a few synthetic pesticides approved for organic farming, used rarely and only as a last choice and coordinated with a USDA organic certifying agent
Organic farming practices for farm animals (livestock) include:
- Healthy living conditions and access to the outdoors
- Pasture feeding for at least 30% of farm animals' nutritional needs during grazing season
- Organic food for animals
- Shots to protect against disease (vaccinations)
Organic or not? Check the label
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has set up an organic certification program that requires all organic food to meet strict government standards. These standards control how such food is grown, handled and processed.
Any product labeled as organic on the product description or packaging must be USDA certified. If it's certified, the producer may also use an official USDA Organic seal.
The USDA says producers who sell less than $5,000 a year in organic food don't need to be certified. These producers must follow the guidelines for organic food production. But they don't need to go through the certification process. They can label their products as organic. But they can't use the official USDA Organic seal.

Products certified 95 percent or more organic may display this USDA seal.
The USDA guidelines describe organic foods on product labels as:
- 100% organic. This label is used on certified organic fruits, vegetables, eggs, meat or other foods that have one ingredient. It may also be used on food items with many ingredients if all the items are certified organic, except for salt and water. These may have a USDA seal.
- Organic. If a food with many ingredients is labeled organic, at least 95% of the ingredients are certified organic, except for salt and water. The items that aren't organic must be from a USDA list of approved additional ingredients. These also may have a USDA seal.
- Made with organic. If a product with many ingredients has at least 70% certified organic ingredients, it may have a "made with organic" ingredients label. For example, a breakfast cereal might be labeled "made with organic oats." The ingredient list must show what items are organic. These products can't carry a USDA seal.
- Organic ingredients. If a product has some organic ingredients but less than 70% of the ingredients are certified organic , the product can't be labeled as organic. It also can't carry a USDA seal. The ingredient list can show which ingredients are organic.
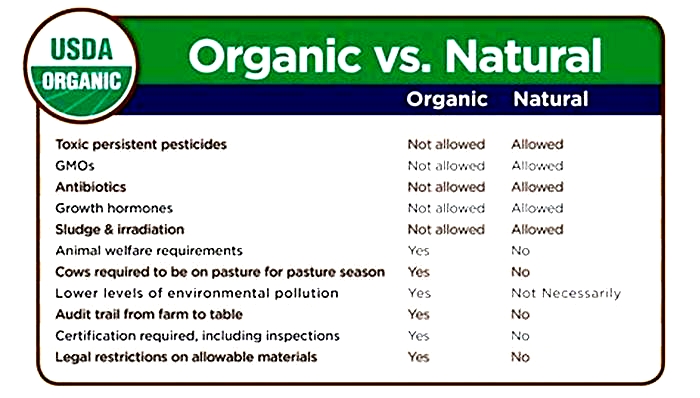
Does 'organic' mean the same thing as 'natural'?
No, "natural" and "organic" are different. Usually, "natural" on a food label means that the product has no artificial colors, flavors or preservatives. "Natural" on a label doesn't have to do with the methods or materials used to grow the food ingredients.
Also be careful not to mix up other common food labels with organic labels. For example, certified organic beef guidelines include pasture access during at least 120 days of grazing season and no growth hormones. But the labels "free-range" or "hormone-free" don't mean a farmer followed all guidelines for organic certification.
Organic food: Is it safer or more nutritious?
Some data shows possible health benefits of organic foods when compared with foods grown using the usual (conventional) process. These studies have shown differences in the food. But there is limited information to prove how these differences can give potential overall health benefits.
Potential benefits include the following:
- Nutrients. Studies have shown small to moderate increases in some nutrients in organic produce. Organic produce may have more of certain antioxidants and types of flavonoids, which have antioxidant properties.
- Omega-3 fatty acids. The feeding requirements for organic farm animals (livestock) usually cause higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids. These include feeding cattle grass and alfalfa. Omega-3 fatty acids a kind of fat are more heart healthy than other fats. These higher omega-3 fatty acids are found in organic meats, dairy and eggs.
- Toxic metal. Cadmium is a toxic chemical naturally found in soils and absorbed by plants. Studies have shown much lower cadmium levels in organic grains, but not fruits and vegetables, when compared with crops grown using usual (conventional) methods. The lower cadmium levels in organic grains may be related to the ban on synthetic fertilizers in organic farming.
- Pesticide residue. Compared with produce grown using usual (conventional) methods, organically grown produce has lower levels of pesticide residue. The safety rules for the highest levels of residue allowed on conventional produce have changed. In many cases, the levels have been lowered. Organic produce may have residue because of pesticides approved for organic farming or because of airborne pesticides from conventional farms.
- Bacteria. Meats produced using usual (conventional) methods may have higher amounts of dangerous types of bacteria that may not be able to be treated with antibiotics. The overall risk of contamination of organic foods with bacteria is the same as conventional foods.
Are there downsides to buying organic?
One common concern with organic food is cost. Organic foods often cost more than similar foods grown using usual (conventional) methods. Higher prices are due, in part, to more costly ways of farming.
Food safety tips
Whether you go totally organic or choose to mix conventional and organic foods, keep these tips in mind:
- Choose a variety of foods from a mix of sources. You'll get a better variety of nutrients and lower your chance of exposure to a single pesticide.
- Buy fruits and vegetables in season when you can. To get the freshest produce, ask your grocer what is in season. Or buy food from your local farmers market.
- Read food labels carefully. Just because a product says it's organic or has organic ingredients doesn't mean it's a healthier choice. Some organic products may still be high in sugar, salt, fat or calories.
- Wash and scrub fresh fruits and vegetables well under running water. Washing helps remove dirt, germs and chemical traces from fruit and vegetable surfaces. But you can't remove all pesticide traces by washing. Throwing away the outer leaves of leafy vegetables can lessen contaminants. Peeling fruits and vegetables can remove contaminants but may also cut nutrients.
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
ErrorEmail field is required
ErrorInclude a valid email address
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Thank you for subscribing!
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription
Please, try again in a couple of minutes
April 22, 2022- Organic production and handling standards. U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://www.ams.usda.gov/publications/content/organic-production-handling-standards. Accessed March 30, 2022.
- Introduction to organic practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://www.ams.usda.gov/publications/content/introduction-organic-practices. Accessed March 30, 2022.
- Organic labeling at farmers markets. U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://www.ams.usda.gov/publications/content/organic-labeling-farmers-markets. Accessed March 30, 2022.
- Labeling organic products. U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://www.ams.usda.gov/publications/content/labeling-organic-products. Accessed March 30, 2022.
- Use of the term natural on food labeling. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition/use-term-natural-food-labeling. Accessed March 30, 2022.
- Demory-Luce D, et al. Organic foods and children. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed March 30, 2022.
- Pesticides and food: Healthy, sensible food practices. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. https://www.epa.gov/safepestcontrol/pesticides-and-food-healthy-sensible-food-practices. Accessed March 30, 2022.
- Vegetable and pulses outlook: November 2021. U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://www.ers.usda.gov/publications/pub-details/?pubid=102664. Accessed March 30, 2022.
- Changes to the nutrition facts label. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition/changes-nutrition-facts-label. Accessed March 30, 2022.
- Rahman SME, et al. Consumer preference, quality and safety of organic and conventional fresh fruits, vegetables, and cereals. Foods. 2021; doi:10.3390/foods10010105.
- Brantsaeter AL, et al. Organic food in the diet: Exposure and health implications. Annual Review of Public Health. 2017; doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031816-044437.
- Vigar V, et al. A systematic review of organic versus conventional food consumption: Is there a measurable benefit on human health? Nutrients. 2019; doi:10.3390/nu12010007.
- Mie A, et al. Human health implications of organic food and organic agriculture: A comprehensive review. Environmental Health. 2017; doi:10.1186/s12940-017-0315-4.
- Innes GK, et al. Contamination of retail meat samples with multidrug-resistant organisms in relation to organic and conventional production and processing: A cross-sectional analysis of data from the United States National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System, 2012-2017. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2021; doi:10.1289/EHP7327.
Should you go organic?
Image: Thinkstock |
These foods are grown without fertilizers, pesticides, and other synthetic additives. But are they better for you?
Walk through any grocery store today, and you'll likely see more shelf space devoted to organicsfoods that are grown without most synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, and animal products that are free of antibiotics and hormones. Demand for organic food is up, with sales reaching $35.9 billion in 2014. "I think people believe these foods are better for them, but we really don't know that they are," says registered dietitian Kathy McManus, director of the Department of Nutrition at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
What's the buzz about?
Organic agriculture aims to preserve natural resources, support animal health and welfare, and avoid most synthetic materials. It's not just a philosophy; the USDA regulates the organic industry with strict standards. The soil where crops are grown must be inspected and shown to be free of most synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, and the crops cannot have been genetically modified. Animals raised on organic farms receive no antibiotics or growth hormones, are given feed that has been grown organically, and are able to roam around outside. Processed organic foods must not contain synthetic additives.
The USDA then certifies organic crops, animal products, and processed foods. Only foods that are 95% organic can carry a "USDA Organic" seal.
Is there a benefit?
While organic foods have fewer synthetic pesticides and fertilizers and are free of hormones and antibiotics, they don't appear to have a nutritional advantage over their conventional counterparts. "There've been a number of studies examining the macro- and micronutrient content, but whether organically or conventionally grown, the foods are really similar for vitamins, minerals, and carbohydrates," says McManus.
According to USDA data, organic foods have fewer pesticide residues than conventionally grown produce. But the amounts for both types of produce are within the level for safe consumption. And it's unclear if the pesticides used in organic farming are safer than nonsynthetic pesticides used in conventional farming. "The verdict is still out about pesticides and fertilizers as far as the long-term impact on health. There are so many other variables in the environment. It's hard to say it's the pesticide on the peach that was the primary cause of a health-related issue," says McManus.
Similarly, we don't have enough information yet to know if the lack of hormones and antibiotics in organic animal products makes them healthier than conventional animal products.
Should you buy it?
McManus says she doesn't recommend organic food to people, but will talk with them about it if they are concerned about pesticides. "At this time, after examining the data, I don't see any nutritional reasons to choose organic foods over conventional," she says.
If you do want to go organic, you'll likely notice a higher price tag on many items, as much as 10% to 50% more than conventional foods.
How do you make the decision about going organic? "It's usually people who are concerned about what's going into food production and who can afford to make the choice for organic," says McManus. Some people intuitively feel that foods with synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, and trace amounts of hormones and antibiotics, likely have adverse health effects, even if that has not been proved. And some people choose organic foods not for health reasons, but because they think they taste better.
Making the switch to organic food
Where would you start if you wanted to go organic? "Produce," says registered dietitian Kathy McManus, director of the Department of Nutrition at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital. Try buying organic versions of foods on the Dirty Dozen list, published each year by the Environmental Working Group (EWG). The list shows USDA findings of conventionally grown foods most likely to contain pesticide residues. This year's list includes apples, celery, cherry tomatoes, cucumbers, grapes, nectarines, peaches, potatoes, snap peas, spinach, strawberries, and sweet bell peppers. Produce items with thicker skins tend to have fewer pesticide residues, because the thick skin or peel protects the inner fruit or vegetable. Remove the skin or peel, and you're removing much of the residue. The EWG puts out a list of those foods, too, called the Clean 15. On the list this year: asparagus, avocados, cabbage, cantaloupe, cauliflower, eggplant, grapefruit, kiwi, mangoes, onions, papayas, pineapples, sweet corn, sweet peas, and sweet potatoes. Image: iStock |

 Organic produce may have fewer pesticide residues than conventionally grown produce. But the amounts for both are within the levels for safe consumption.
Organic produce may have fewer pesticide residues than conventionally grown produce. But the amounts for both are within the levels for safe consumption.